在上一篇博客学习了GadgetInspector的核心逻辑,当然网上还有很多优化版本,这里学习了5wimming师傅的版本https://github.com/5wimming/gadgetinspector
还有主要参考了su18师傅的这篇https://su18.org/post/gadgetor, 但是作者好像没公布他的工具。
继承方法
之前说到这个methodImplMap结构为{某方法:{它的所有重写方法}}, 然后作为构造参数传给了ImplementationFinder。所以这就导致在这一步:
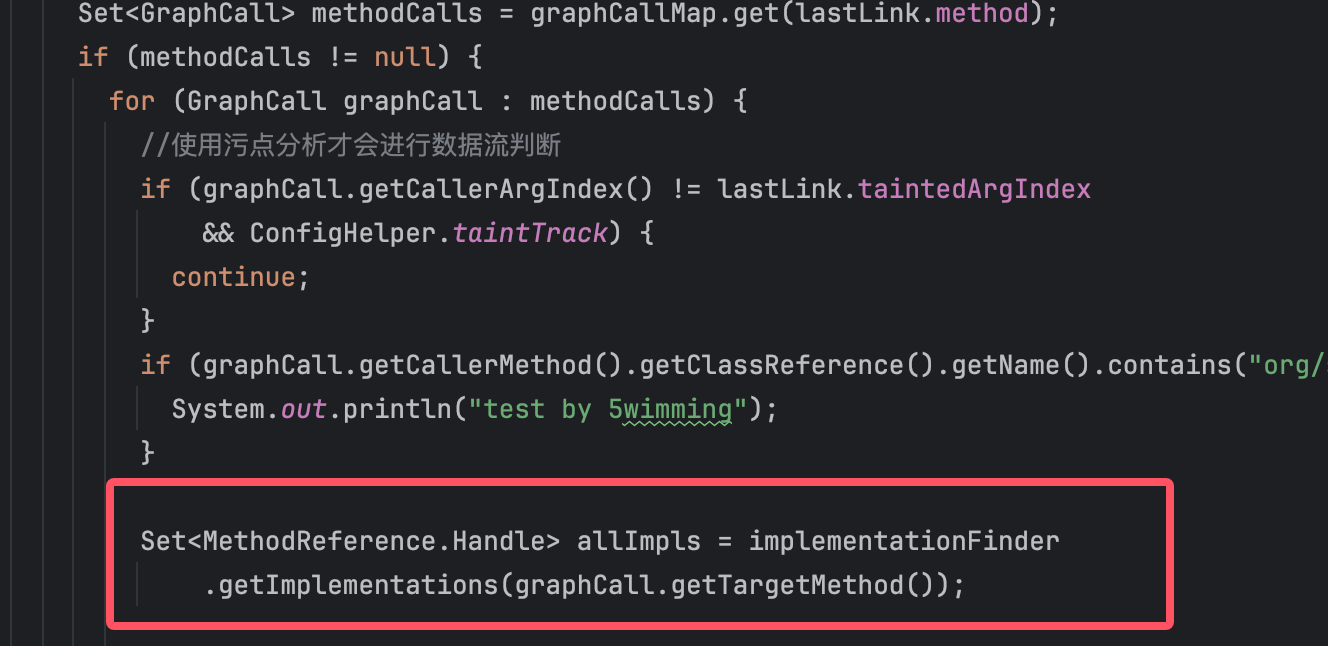
并不会查找到从父类继承过来的方法,这样就会导致一些链子找不到。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| if (allImpls.isEmpty()) {
Set<ClassReference.Handle> parents = inheritanceMap.getSuperClasses(graphCall.getTargetMethod().getClassReference());
if (parents == null)
continue;
for (ClassReference.Handle parent : parents) {
Set<MethodReference.Handle> methods = methodsByClass.get(parent);
if (methods == null)
continue;
for (MethodReference.Handle method : methods) {
if (method.getName().equals(graphCall.getTargetMethod().getName()) && method.getDesc().equals(graphCall.getTargetMethod().getDesc())) {
allImpls.add(method);
}
}
}
}
|
这里就修复了这个bug,在allImpls为空时,去methodByClass查找methods。如果还找不到,就continue。找到了,就加入allImpls。
路径爆炸
字面意思,结果出现了太多,太长的路径,重复的,循环调用的。
分支过长
加入了这个参数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
if (exploredMethodsMap.containsKey(newLink)){
if(exploredMethodsMap.get(newLink) > ConfigHelper.maxRepeatBranchesTimes){
continue;
}
exploredMethodsMap.put(newLink, exploredMethodsMap.get(newLink)+1);
}
|
默认20,超过就舍弃掉这个链。
链聚合优化
例如 A -> B -> C , E -> C -> D ,可以链聚合优化为A->B->C->D
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
Set<GadgetChain> tmpDiscoveredGadgets = new HashSet<>();
for (GadgetChain gadgetChain : methodsToExploreRepeat) {
GadgetChainLink lastLink = gadgetChain.links.get(gadgetChain.links.size() - 1);
for (GadgetChain discoveredGadgetChain : discoveredGadgets) {
boolean exist = false;
for (GadgetChainLink gadgetChainLink : discoveredGadgetChain.links) {
if (exist) {
gadgetChain = new GadgetChain(gadgetChain, gadgetChainLink);
}
if (lastLink.equals(gadgetChainLink)) {
exist = true;
}
}
if (exist) {
tmpDiscoveredGadgets.add(gadgetChain);
}
}
}
discoveredGadgets.addAll(tmpDiscoveredGadgets);
|
算法流程:
还是刚刚的例子,比如链A->B->C, lastLink是C
遍历E->C->D所有节点,判断lastLink是否与其相等。相等exist赋值为true,合并为新链A->B->C->D,在循环结束后加入结果里。
路径爆炸
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| if (ConfigHelper.similarLevel > 0){
TreeSet<GadgetChain> treeSimilar = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<GadgetChain>() {
@Override
public int compare(GadgetChain o1, GadgetChain o2) {
int compareResult = o1.links.size() - o2.links.size();
if (compareResult == 0){
return -1;
}
return compareResult;
}
});
for (GadgetChain chain : discoveredGadgets) {
if (chain.links.size() <= ConfigHelper.similarLevel){
continue;
}
treeSimilar.add(chain);
}
if (!treeSimilar.isEmpty()){
Set<ArrayList<GadgetChainLink>> repeatSim = new HashSet<>();
for (GadgetChain chain : treeSimilar){
ArrayList<GadgetChainLink> temp = new ArrayList<>(chain.links.subList(0,ConfigHelper.similarLevel));
temp.add(chain.links.get(chain.links.size()-1));
if(repeatSim.contains(temp)){
discoveredGadgets.remove(chain);
}
else {
repeatSim.add(temp);
}
}
}
}
|
但其实这个解决方法有点太简便了,它只解决了开头重复。比如说是:
A->B->C->D, A->B->C->E, 我们设置similarLevel 为3
那么遍历到第一条链子时把A->B->C加入repeatSim。遍历到第二条链子时,发现重复,就把第二条删了。
Source/Sink优化
sink就不说了,添加了各种类型漏洞的sink。我比较感兴趣的是web项目的source怎么定义。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| if (!method.getName().contains("<init>")
&& (method.getDesc().contains("Ljavax/servlet/http/HttpServletRequest")
|| method.getDesc().contains("Ljavax/servlet/ServletRequest")
|| method.getDesc().contains("Ljavax/xml/ws/handler/soap/SOAPMessageContext")
|| method.getDesc().contains("Ljavax/xml/ws/handler/MessageContext")
|| method.getDesc().contains("Ljavax/xml/rpc/handler/soap/SOAPMessageContext")
|| method.getDesc().contains("Lorg/apache/cxf/message/Message")
|| method.getDesc().contains("Lorg/aopalliance/intercept/MethodInvocation")
|| methodValue.getMethodAnnotationDesc().contains("Lorg/springframework/web/bind/annotation/RequestMapping")
|| methodValue.getMethodAnnotationDesc().contains("Ljavax/ws/rs/Path")
|| methodValue.getMethodAnnotationDesc().contains("Lorg/springframework/web/bind/annotation/GetMapping")
|| methodValue.getMethodAnnotationDesc().contains("Lorg/springframework/web/bind/annotation/PostMapping")
|| methodValue.getParameterAnnotationDesc().contains("Lorg/springframework/web/bind/annotation/RequestParam")
|| methodValue.getMethodAnnotationDesc().contains("Lorg/springframework/web/bind/annotation/PutMapping")
|| methodValue.getMethodAnnotationDesc().contains("Lorg/springframework/web/bind/annotation/PatchMapping")
|| methodValue.getParameterAnnotationDesc().contains("Lorg/springframework/web/bind/annotation/DeleteMapping")
|| methodValue.getParameterAnnotationDesc().contains("Ljavax/ws/rs/QueryParam")
|| methodValue.getParameterAnnotationDesc().contains("Ljavax/ws/PathParam")))
{
addDiscoveredSource(new Source(method, 0));
}
|
看java原生的source定义,和HttpServletRequest有关的,就作为source。
因为各种参数都放在这里面,如果调用它,很可能是用户从中获取的数据。但感觉会有误报。
然后另一类型是注解修饰的,比如Springboot,@RequestMapping注解修饰的方法,其参数是用户输入,所以这些方法也作为source。
框架众多,而各种source和sink也总结的比较全,就不再赘述了。
